Introduction:
Zhou Ji, president of Chinese Academy of Engineering: intelligent production is the main line of intelligent manufacturing, and intelligent factory is the main carrier of intelligent production.
Intelligent factory construction mode :(1) from the digital production process to the intelligent factory; (2) from the intelligent manufacturing production unit (equipment and products) to the intelligent factory; (3) from personalized customization to the interconnected factory
First, the connotation and construction focus of intelligent factory
Intelligent factory is an important carrier to realize intelligent manufacturing. The intelligent production process is realized mainly through the construction of intelligent production system and network distributed production facilities. Smart factories have autonomous capabilities, which can be collected, analyzed, judged and planned; Inference and prediction are made through holistic visual technology, and simulation and multimedia technology are used to amplify the design and manufacturing process in real life. Each component of the system can form the best system structure by itself, with the characteristics of coordination, reorganization and expansion. The system has been equipped with self-learning, self-maintenance ability. Therefore, intelligent factory realizes the mutual coordination and cooperation between man and machine, and its essence is human-machine interaction.
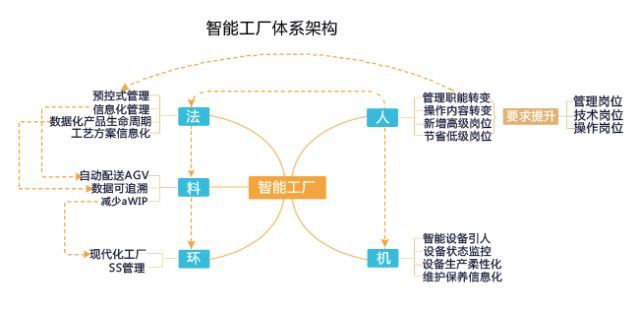
Man-machine material method loop is the abbreviation of the five main factors affecting product quality in total quality management theory. Person refers to the person who manufactures the product; Machine, equipment used to manufacture products; Material refers to the raw materials used in the manufacture of products; Method refers to the method used to manufacture the product; Ring refers to the environment in which the product is manufactured. The intelligent production is a multi-dimensional integration process that takes the intelligent factory as the core and connects people, machines, methods, materials and rings.
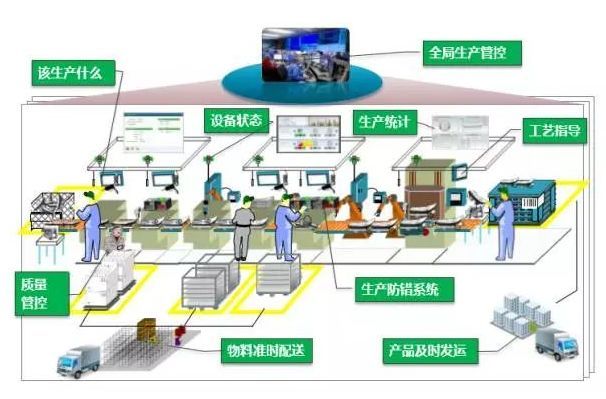
In the architecture of the smart factory, the five elements of quality management will change accordingly, because in the smart factory of the future, people, machines, and resources will be able to communicate with each other. Smart products "know" the details of how they are made and what they are used for. They will actively answer questions about the manufacturing process such as "when I was made", "what parameters should be used to process me", "where should I be sent" and so on.
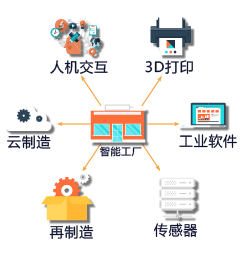
The intelligent factory prototype built by enterprises based on CPS and industrial Internet mainly includes the physical layer, the information layer, the big data layer, the industrial cloud layer and the decision layer. Among them, the physical layer contains hardware devices of different levels in the factory, from the smallest embedded devices and basic components to sensing devices, manufacturing devices, manufacturing units and production lines, which are interconnected with each other. Based on this, a vertical integrated environment is built, which can be measured, controlled, produced and managed. The information layer covers all links of enterprise business, including various business management activities such as R&D, design, manufacturing, marketing services, logistics and distribution, as well as the resulting mass innovation, personalized customization, e-commerce, visual tracking and other related businesses. On this basis, the horizontal integrated environment of enterprise internal value chain is formed to realize the flow and exchange of data and information.
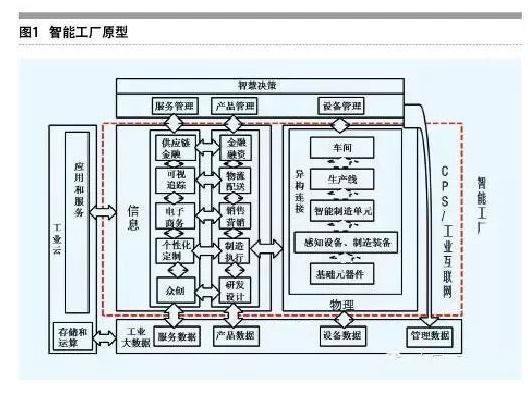
Vertical integration and horizontal integration are based on the CPS and the Internet industry, product, equipment, manufacturing units, production lines, workshop, factory manufacturing system such as connectivity, and the different part of the integration of the business enterprise, by data applications and industrial cloud service implementation, and policy makers based on products, services, support enterprise equipment management is the most high. Together, they build a complete value network system of a smart factory and provide end-to-end solutions for users.
Due to the obvious difference of product manufacturing process, discrete manufacturing industry and process manufacturing industry have different key contents in the construction of intelligent factory. For discrete manufacturing, products are usually assembled by multiple parts and components through a series of discontinuous processes, and the process contains many changes and uncertainties, which to some extent increases the difficulty and complexity of discrete manufacturing production organization. Enterprises often arrange the location of production equipment according to the main process flow to minimize the transfer distance of materials. Order-oriented discrete manufacturing enterprises have the characteristics of multiple varieties and small batches, and their process routes and equipment use are more flexible. Therefore, discrete manufacturing enterprises pay more attention to the flexibility of production, and the construction of intelligent factories focuses on intelligent manufacturing production lines.
Second, the main construction mode of smart factory
Due to the different production processes of various industries and the different intelligent conditions of various industries, smart factories have the following different construction modes.
The first model is the digitization of production processes to smart factories. In petrochemical, iron and steel, metallurgy, building materials, textile, paper, medicine, food and other process manufacturing fields, the internal motivation for enterprises to develop intelligent manufacturing lies in product quality control, focusing on starting from the digital construction of production, based on the quality control demand from the end of product control to the whole process control.
The second model is from smart manufacturing production units (equipment and products) to smart factories. In discrete manufacturing fields such as machinery, automobile, aviation, shipbuilding, light industry, household appliances and electronic information, the core purpose of enterprises to develop intelligent manufacturing is to expand the product value space, focusing on the automation of single equipment and product intelligence, based on the improvement of production efficiency and product efficiency to achieve value growth.
The third model is from personalized customization to connected factories. In the field of consumer goods manufacturing that is closest to users, such as home appliances, clothing and home furnishing, enterprises focus on the development of intelligent manufacturing to fully meet the diversified needs of consumers while realizing the production of economies of scale, and focus on carrying out large-scale personalized customization model innovation through the Internet platform.
III. Key links in the development of smart factories
Intelligent production focuses on applying advanced technologies such as human-computer interaction and 3D printing to the entire industrial production process, and monitoring and data collection of the entire production process to facilitate data analysis, so as to form a highly flexible, personalized and networked industrial chain.

3 d printing
3D printing is a disruptive innovation that has been called the most important manufacturing technology innovation of the 20th century by the National Science Foundation. The whole process of manufacturing can be introduced with 3D printing to save costs, speed up progress and reduce material waste. In the design process, with the help of 3D printing technology, designers can obtain greater freedom and creative space, and can focus on the creative form and functional innovation of products without considering the impact of shape complexity, because 3D printing can almost complete the construction of any shape of objects. In the production link, 3D printing can directly generate parts from the digital model, without the need for special processes such as mold making, which not only saves costs, but also speeds up the launch of products. In addition, whereas traditional manufacturing processes typically produce waste from casting, polishing and assembling parts, 3D printing can shape the same parts in one go, creating little waste. In distribution, 3D printing could challenge existing logistics distribution networks. In the future, parts will no longer need to be sourced and shipped from the original manufacturer. Instead, 3D printed model files will be downloaded from the manufacturer's online database and quickly printed locally, which could render the global warehousing and distribution system of parts meaningless.
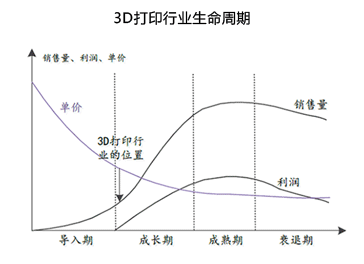
After nearly 40 years of development, leading 3D printing companies have begun to achieve significant profits, market recognition has risen rapidly, and industry revenue growth has accelerated. According to the typical product life cycle theory, technical products often show the characteristics of accelerated growth in the process from the introduction period to the growth period, which indicates that the 3D printing industry is entering the accelerated growth period at present.
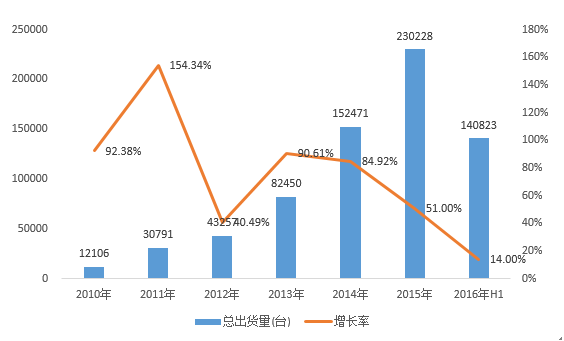
Figure: Growth in shipments of global 3D printing equipment from 2008 to 2015
The whole industry chain of 3D printing industry can be roughly divided into three parts: the upstream basic parts industry, 3D printing equipment production enterprises, 3D printing materials production enterprises and supporting enterprises; the downstream mainly covers various application fields of 3D printing. Generally speaking, the 3D printing industry mainly refers to 3D printing equipment, materials and service enterprises.
Figure: 3D printing industry chain
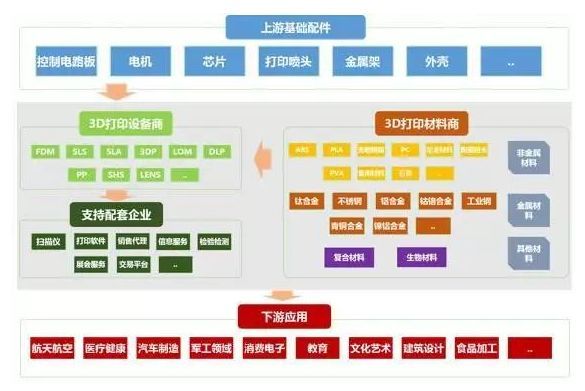
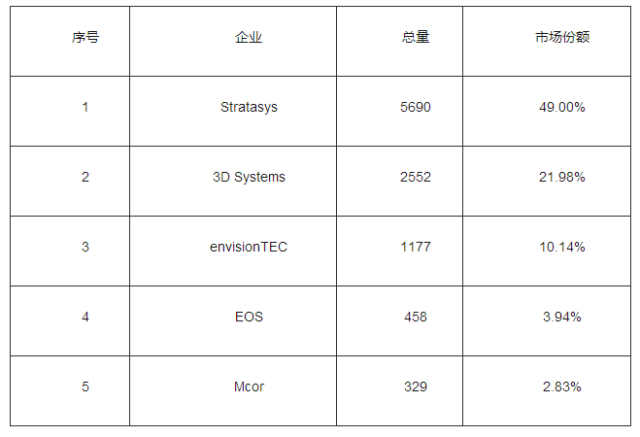
3D printing has formed a complete industrial chain. Each link of the industry chain has gathered a number of leading enterprises. Globally, equipment enterprises represented by Stratasys and 3D Systems play a leading role in the industrial chain, and these equipment enterprises are usually able to provide material and printing services, such as having a strong voice.
Table: Top 5 enterprises of industrial/professional 3D printing equipment shipment in 2015

The human-computer interaction
In the future, all kinds of interactions will be deeply integrated, so that smart devices will more naturally synchronize with human biological reactions and processing processes, including thought processes, kinesthetic processes, and even one's cultural preferences. This field is full of all kinds of novel possibilities.

With the quickened pace of technological integration, the information exchange mode between man and machine is advancing to a higher level, and the new man-machine interaction mode is gradually applied in the field of production and manufacturing. Specific performance in the intelligent interactive equipment flexibility and intelligent interactive equipment industrial application of these two aspects. In the production process, the intelligent manufacturing system can independently undertake tasks such as analysis, judgment and decision-making, highlighting the core role of human in the manufacturing system. At the same time, with the cooperation of industrial robots, trackless AGVs and other intelligent equipment, the potential of human can be better exerted. Machine intelligence and human intelligence are truly integrated and complement each other. It's essentially man-machine integration.
传感器
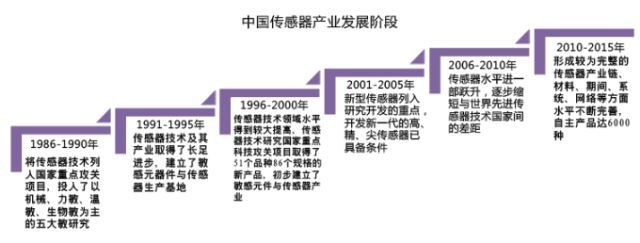
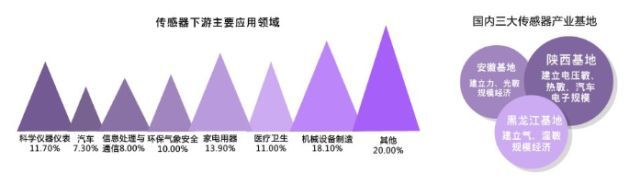
China has basically formed a relatively complete industrial chain structure, in materials, devices, systems, network and other aspects of the level of continuous improvement, the independent products have reached 6,000 kinds, the country has set up three sensor production bases, respectively: Anhui base, Shaanxi base and Heilongjiang base. The government has put forward guidelines to accelerate the development of domestic sensor industry, and the sensor development will be improved in the direction of intelligence in the future.
Industrial software
The construction of intelligent factory is inseparable from the wide application of industrial software. Industrial software includes basic software and application software. Among them, system, middleware and embedded software belong to the scope of basic technology and are not closely related to the specific industrial management process and technological process. The industrial software mentioned below mainly refers to application software, including operation management software, production management software and R&D and design software.
Under the background of "Made in China 2025", it has become the general trend for industrial enterprises to change their development mode and accelerate the integration of the two industries. The demand for industrial software and information services will continue to increase, and China will continue to maintain its position as a new force in the global industrial software market growth.
Specifically, in China's industrial software industry in 2016, product R&D, such as CAD, CAE, CAM, CAPP, etc., accounted for about 8.3%, while information management, such as ERP, CRM, HRM, accounted for about 15.5%. Production control such as MES, PCS, PLC accounted for about 13.2%; The remaining 63% are embedded software development.
In terms of regions, North China and East China are the regions with the most industrial software applications, accounting for about half of the country. Specifically, Beijing, Shanghai, Guangdong and Jiangsu are regions with strong industrial software, accounting for more than half of China's industrial software market size.
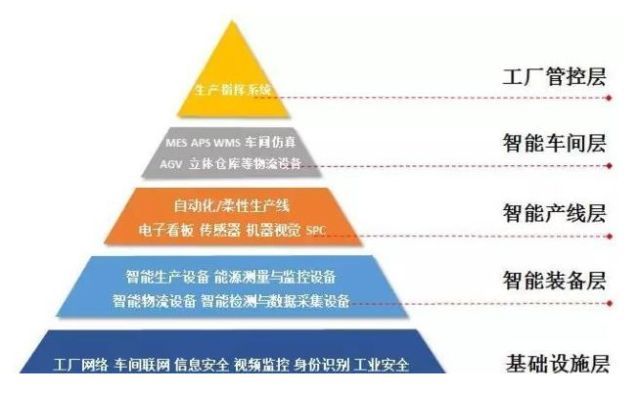
Widely used in MES (Manufacturing Execution System), APS (Advanced Production Scheduling), PLM(Product Life Cycle Management), ERP(Enterprise Resource Planning), quality management and other industrial software, to achieve the visualization and transparency of the production site. In the new factory, the digital factory simulation software can be used to simulate the layout of equipment and production line, factory logistics, ergonomics, etc., to ensure the reasonable structure of the factory. Data security and equipment and automation systems must be ensured as the digital transition progresses. In the detection of defective products through professional testing equipment, not only to be able to automatically and qualified products shunting, but also through SPC (statistical process control) and other software, to analyze the cause of quality problems.
Cloud manufacturing
Cloud manufacturing means that manufacturing enterprises integrate advanced information technology, manufacturing technology and emerging Internet of Things technology, etc., and the data of factory capacity and process are concentrated on the cloud platform. Manufacturers can carry out big data analysis and customer relationship management in the cloud, so as to give full play to the best performance of enterprises.

The picture shows the concept of cloud manufacturing and the process from traditional manufacturing, to smart manufacturing, to smart manufacturing, to today's cloud manufacturing.
In China, we can see the group enterprise cloud manufacturing service platform for complex aerospace products developed by China Aerospace Science and Industry Corporation, which is connected with the rich manufacturing resources and capabilities of the affiliated institutes and bases of the Group. CRRC Group's cloud manufacturing service platform for rail transit equipment has opened up the R & D, design, manufacturing, repair and service of rail vehicles, construction machinery, electromechanical equipment, electronic equipment and related components. Cloud manufacturing platforms for small and medium-sized enterprises have also emerged in equipment manufacturing, bags, shoes and hats and other industries.
Cloud manufacturing provides a new concept and mode for manufacturing informationization. Cloud manufacturing, as a nascent concept, has a huge space for development in the future. But the future development of cloud manufacturing is still faced with many key technical challenges, in addition to cloud computing, Internet of things, the semantic Web, high-performance computing, embedded system technology such as integrated, based on the knowledge of manufacture resource in the cloud, the cloud management engine, cloud manufacturing application collaboration, cloud manufacturing visualization and user interface technology is an important technology of the future need to overcome.
conclusion
The construction of intelligent factory is undoubtedly an important way for manufacturing enterprises to transform and upgrade. At the same time, the construction blueprint of intelligent factory should be reasonably planned based on the medium and long term development strategy of enterprises and the characteristics of their own products, processes, equipment and orders. On the basis of promoting standardization and standardization, the construction of intelligent factories should be promoted pragmatically from the point of view of the most urgent problems to be solved.
